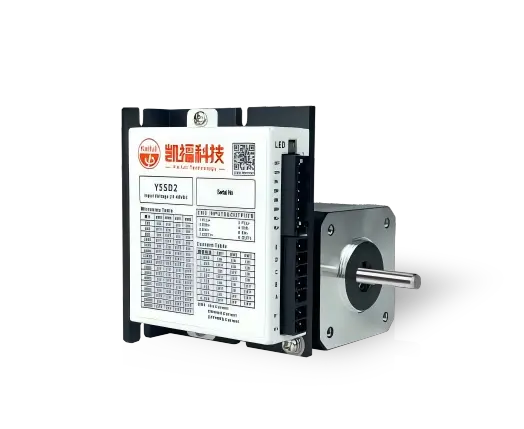
Why do we use stepper motor instead of DC motor?
When it comes to choosing a motor for precision applications, Stepper Motors are often preferred over traditional DC motors. While both types of motors serve as reliable sources of motion, stepper motors offer distinct advantages that make them the go-to choice in many applications requiring accuracy, control, and reliability. Below, we explore the reasons why stepper motors are commonly used instead of DC motors.
1. Precision and Accuracy
One of the primary reasons stepper motors are preferred over DC motors is their ability to provide precise and controlled movement. Stepper motors divide a full rotation into equal, discrete steps, making them ideal for applications that require accurate positioning.
Key Benefits:
- Fixed Step Angles: Stepper motors move in fixed increments, such as 1.8° or 0.9° per step, ensuring highly accurate positioning without needing feedback mechanisms.
- Repeatability:The stepper motor's Open-Loop Control system allows it to repeat its movements consistently with minimal deviation.
In contrast, DC motors provide continuous rotation and require external encoders or feedback systems to achieve similar precision, which can complicate the design and increase costs.
Applications Requiring Precision:
- 3D Printers: Stepper motors are essential for precise control of the print head and bed.
- CNC machines: They control cutting tools and positioning systems with high accuracy.
2. High Torque at Low Speeds
Stepper motors are known for delivering high torque at low speeds, a feature that makes them especially suitable for applications that demand slow, controlled movement without sacrificing performance.
Advantages for Low-Speed Operation:
- Stepper motors maintain their torque even at low speeds, unlike DC motors, which tend to lose torque as their speed decreases.
- This makes stepper motors ideal for applications like robotics, camera stabilization, and automated machinery.
In applications where controlled and consistent low-speed movement is required, stepper motors outperform DC motors, which require gearboxes or other mechanisms to maintain torque at lower speeds.
3. No Need for Feedback Systems
Another reason stepper motors are favored over DC motors is that they can operate in an open-loop control system. This means that stepper motors do not require additional feedback systems such as encoders or tachometers to maintain their position or speed.
Why is this important?
- Cost Efficiency: Open-loop control simplifies the design and reduces the overall cost of the system since no complex feedback mechanisms are needed.
- Reliability: Fewer components mean less risk of failure, making stepper motors a more robust and reliable solution.
On the other hand, DC motors generally require feedback loops to ensure accurate speed and position control, adding complexity and increasing costs.
4. Better for Precise Positioning in Robotics and Automation
In robotic systems and automated machinery, precise positioning is often a critical factor. Stepper motors excel in these environments due to their ability to control movement with great accuracy.
Common Applications:
- Robotic Arms: Stepper motors control the movement of robotic arms for tasks such as assembly, welding, and packaging.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Stepper motors allow for precise navigation and positioning of AGVs in warehouses and factories.
For these tasks, stepper motors' predictable and repeatable movements are essential, while DC motors would require additional components to achieve the same level of precision.
5. Simple Control and Integration
Stepper motors are relatively easy to control and integrate into systems. Unlike DC motors, which require complex controllers to regulate speed and direction, stepper motors can be controlled directly by pulse signals.
Benefits of Simple Control:
- Ease of Integration: Stepper motors can be easily integrated into control systems without needing complex hardware.
- Precise Speed Control: The speed of a stepper motor is directly proportional to the frequency of the input pulses, allowing for straightforward control of both speed and position.
This simplicity makes stepper motors a preferred choice in applications that need quick and reliable motion control, like in printers, scanners, and camera equipment.
Conclusion
While DC motors are reliable for continuous rotation and basic applications, stepper motors are the better choice when precision, reliability, and control are critical. Their ability to deliver precise step-based movements without requiring complex feedback systems makes them ideal for 3D printing, robotics, medical devices, and more. Whether you need high torque at low speeds or an easy-to-integrate solution for precise positioning, stepper motors provide the advantages needed to meet these requirements.




 Daniel.Ding
Daniel.Ding Ding
Ding