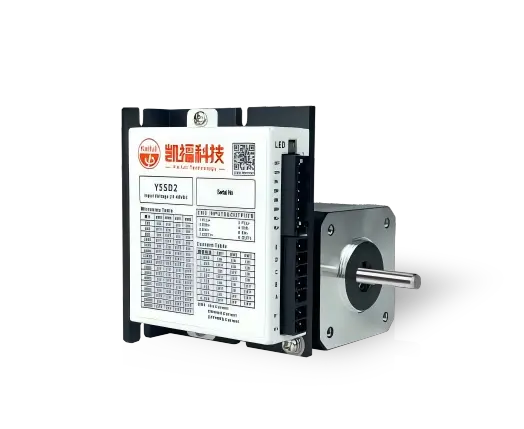
What is the difference between a stepper motor and a normal motor?
Motors play a vital role in modern technology, powering devices from household appliances to industrial machinery. While “normal motor” is a general term often used to describe standard DC or AC motors, Stepper Motors are a specific type designed for precision and control. This article highlights the key differences between stepper motors and normal motors, helping you understand their unique functionalities and applications.
1. Motion Control
Stepper Motor:
A stepper motor divides a full rotation into discrete steps, making it ideal for applications requiring precise control. Each step represents a fixed degree of rotation, enabling accurate positioning without feedback mechanisms.
Normal Motor:
Normal motors, such as DC or AC motors, provide continuous rotation. They are not designed for incremental movement and require additional components like encoders for precision control.
2. Speed and Torque Characteristics
Stepper Motor:
- Delivers high torque at low speeds, making it suitable for tasks requiring precise, slow movement.
- Torque decreases significantly as speed increases.
Normal Motor:
- Provides consistent torque over a wider speed range.
- Excels in high-speed, high-power applications.
3. Control System
Stepper Motor:
- Operates in an Open-Loop Control system, where position and movement are determined by input pulses.
- Does not require feedback, simplifying its design for precision tasks.
Normal Motor:
- Often operates in a closed-loop system for advanced applications, using feedback devices like sensors or encoders to regulate speed and position.
4. Efficiency and Power Requirements
Stepper Motor:
- Consumes power even when holding a position, which can reduce efficiency.
- Ideal for low-power, high-precision applications like 3D printers and CNC machines.
Normal Motor:
- Generally more efficient in continuous operation scenarios.
- Designed for high-power tasks such as driving fans, pumps, and industrial machinery.
5. Applications
Stepper Motor Applications:
- Robotics: For precise movement and positioning.
- 3D Printing: Layer-by-layer precision in manufacturing.
- CNC Machines: Controlled cutting and milling.
- Medical Devices: Precision movement in equipment like infusion pumps.
Normal Motor Applications:
- Household Appliances: Fans, washing machines, and refrigerators.
- Automotive: Electric windows, wipers, and cooling systems.
- Industrial Equipment: Conveyor belts, mixers, and compressors.
6. Cost and Complexity
Stepper Motor:
- Typically more affordable and easier to control for applications requiring precision.
- Requires a stepper driver for operation.
Normal Motor:
- Cost depends on the motor type and additional components like controllers.
- More complex systems may incur higher costs for advanced control features.
Conclusion
The choice between a stepper motor and a normal motor depends on the specific needs of your application. Stepper motors excel in precision, repeatability, and low-speed torque, making them ideal for projects like robotics and 3D printing. Normal motors, whether DC or AC, are better suited for continuous rotation, high-speed tasks, and power-demanding applications.




 Daniel.Ding
Daniel.Ding Ding
Ding